 2025.12.19
2025.12.19
 News
News
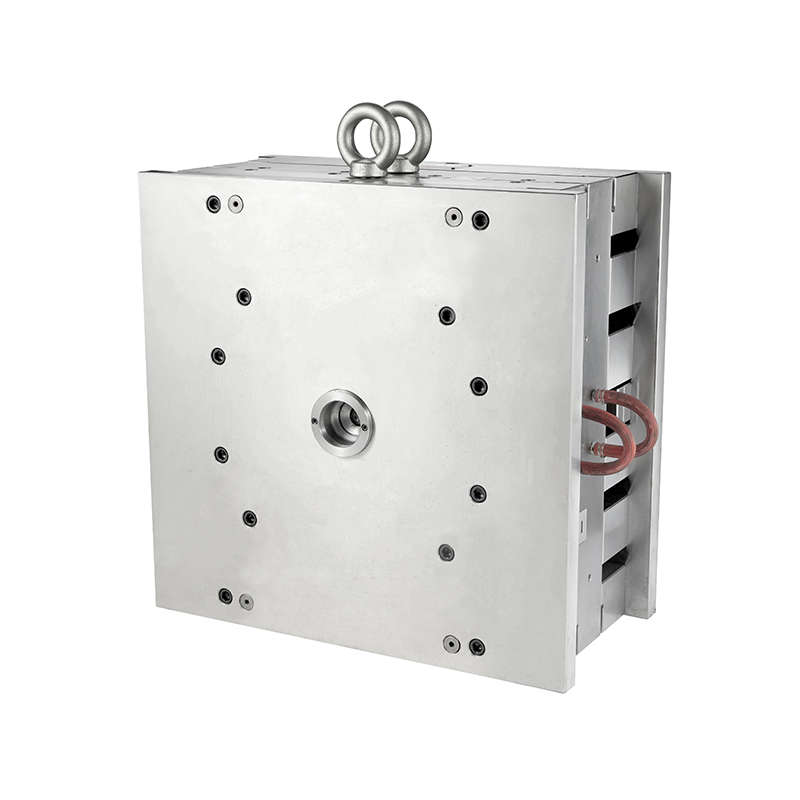
Threaded head cable tie molds are critical tools in producing cable ties with a locking mechanism that ensures secure bundling of wires and other materials. The structural design of these molds directly affects the quality, efficiency, and reliability of the manufactured cable ties. A well-designed mold balances precision, material flow, and ease of maintenance. This essay discusses several aspects of structural design considerations for threaded head cable tie molds, organized under clear subheadings and supplemented with a table for reference.

1. Mold Cavity Design
The mold cavity determines the shape and dimensions of the cable tie, including the head, body, and tail. For a threaded head cable tie, the head contains a locking mechanism with a ratchet or pawl system. The cavity must be accurately machined to ensure precise replication of this mechanism.
Factors to consider in cavity design include:
2. Runner and Gate System
The runner and gate system guides molten polypropylene or other thermoplastic materials into the mold cavity. Its design affects flow uniformity, cycle time, and the likelihood of defects such as incomplete filling or sink marks.
Key considerations include:
3. Ejection Mechanism
Ejection mechanisms remove the finished cable tie from the mold without damage. For threaded head designs, careful attention is required to avoid deforming the locking head or threads.
Common ejection methods include:
The ejection system must be synchronized with mold opening to prevent any mechanical stress on the cable tie.
4. Material Selection and Wear Resistance
Mold materials need to withstand repeated thermal cycles and high injection pressures. Typical choices include hardened steel, pre-hardened steel, or aluminum for prototype molds.
Considerations include:
5. Structural Design Summary Table
The following table summarizes key structural design elements for threaded head cable tie molds and their considerations:
|
Structural Element |
Considerations |
Purpose |
|
Mold cavity |
Tolerance, surface finish, cooling channels |
Shape and precision of cable tie |
|
Runner and gate system |
Runner type, gate position, flow balancing |
Uniform material flow and cycle efficiency |
|
Ejection mechanism |
Pin, air, or slide type; synchronization |
Safe removal of parts without deformation |
|
Material selection |
Hardness, corrosion resistance, thermal conductivity |
Longevity and consistent production quality |
|
Cooling system |
Channel placement, flow rate, uniformity |
Prevents warping and ensures dimensional stability |
6. Additional Design Considerations
In addition to the main structural components, several auxiliary aspects contribute to mold performance: