 2026.01.23
2026.01.23
 News
News
The design of a precision mold is fundamentally driven by the requirement to control variation. Unlike a standard mold, where tolerances might be measured in hundredths of an inch or tenths of a millimeter, precision molds are designed and machined to tolerances often specified in microns (thousandths of a millimeter). This begins with the part design itself, which must be optimized for manufacturability, considering uniform wall thickness to minimize warpage and appropriate draft angles for part ejection. The mold design must account for the predictable shrinkage of the specific plastic material being used, building this compensation directly into the cavity dimensions. Every component, from the cavity and core blocks to the ejector pins and guide pillars, is manufactured to these ultra-fine tolerances. The design also prioritizes thermal management, with meticulously engineered cooling channels to ensure uniform and rapid heat extraction, which is a primary factor in controlling part warpage and cycle time.
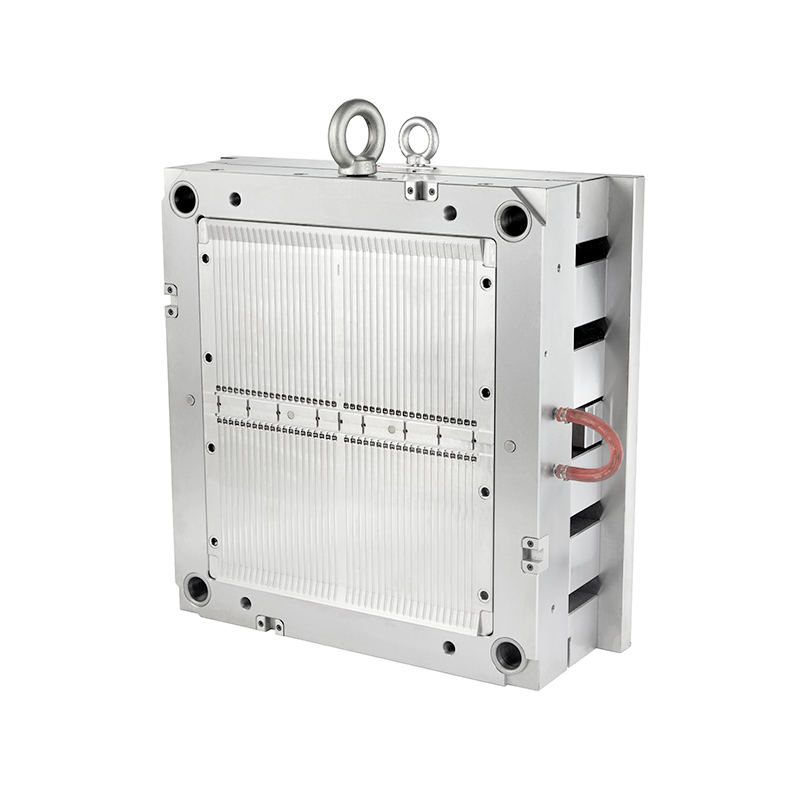

The construction of a precision mold utilizes high-grade materials and components to maintain stability under repeated cycles of heat, pressure, and mechanical stress.
|
Component Category |
Specific Examples & Materials |
Primary Function in Precision Context |
|
Mold Base |
Standardized plates (A & B plates, support plates) made from pre-hardened steel like P20 or 4140. |
Provides a rigid, aligned foundation to house the custom cavity and core. Maintains dimensional stability under clamp force. |
|
Cavity & Core Inserts |
Machined from high-hardness, polished tool steels such as H13, S7, or stainless steels (for corrosion resistance). Often hardened to 48-52 HRC after machining. |
Form the actual part geometry. High hardness resists wear from abrasive plastics and maintains polished surface finish over long runs. |
|
Ejection System |
Ejector pins, sleeves, and blades made from hardened steel. |
Removes the cooled part without marking or distorting it. Precision-ground pins ensure smooth operation and minimal flash. |
|
Guiding & Alignment |
Guide pins, bushings, and interlocks made from hardened tool steel. |
Ensures perfect alignment of the two mold halves every cycle, critical for maintaining part tolerances and preventing flash. |
|
Temperature Control |
Cooling channels drilled or milled into the mold plates and inserts. May use beryllium copper inserts for fast heat transfer in local areas. |
Precisely manages mold temperature to control cooling rate and minimize internal stress in the plastic part. |
The creation of a precision mold involves advanced machining and finishing techniques that go beyond standard mold making. The cavity and core are typically roughed out using CNC milling and then finished using processes that achieve the required surface finish and dimensional accuracy. Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM), particularly wire EDM and sinker EDM, is extensively used to create intricate details, sharp corners, and deep ribs that are difficult to achieve with milling alone. High-speed CNC machining is employed for fine detailing and to achieve excellent surface finishes directly from the tool. After machining, critical surfaces undergo precision grinding to achieve flatness and parallelity. The most critical step is polishing and texturing. Optical-quality parts may require a mirror polish, achieved through a progressive series of abrasive steps down to diamond paste. Alternatively, specified surface textures are applied via photochemical etching or laser texturing to achieve exact matte finishes or patterns. Every step is followed by meticulous measurement using coordinate measuring machines (CMM) and optical comparators to verify dimensions against the original CAD data.
The performance of a precision mold is realized within the context of the injection molding process and production environment. The mold must be paired with an injection molding machine capable of precise control over injection speed, pressure, and temperature. Process parameters are meticulously developed and documented to ensure repeatability. During production, factors such as ambient temperature and humidity are often controlled to minimize their influence. Quality assurance is continuous, involving frequent measurement of critical part dimensions using statistical process control (SPC) methods to detect any drift that might indicate mold wear or process variation. Maintenance is scheduled and preventative rather than reactive. This includes regular cleaning of vents and cooling lines, lubrication of moving components, and inspection of wear surfaces. Even with robust materials, eventual wear on sealing surfaces, guide components, and ejector systems will necessitate refurbishment to restore the mold to its original precision specifications, ensuring the longevity of the tool and the consistency of the parts it produces.