 2025.06.06
2025.06.06
 News
News
The design of the cable tie mould is crucial to the performance of the cable tie itself. A well-crafted mould ensures that the ties are uniform in size, strength, and quality. It also affects the overall production efficiency, cycle time, and the cost-effectiveness of the manufacturing process.
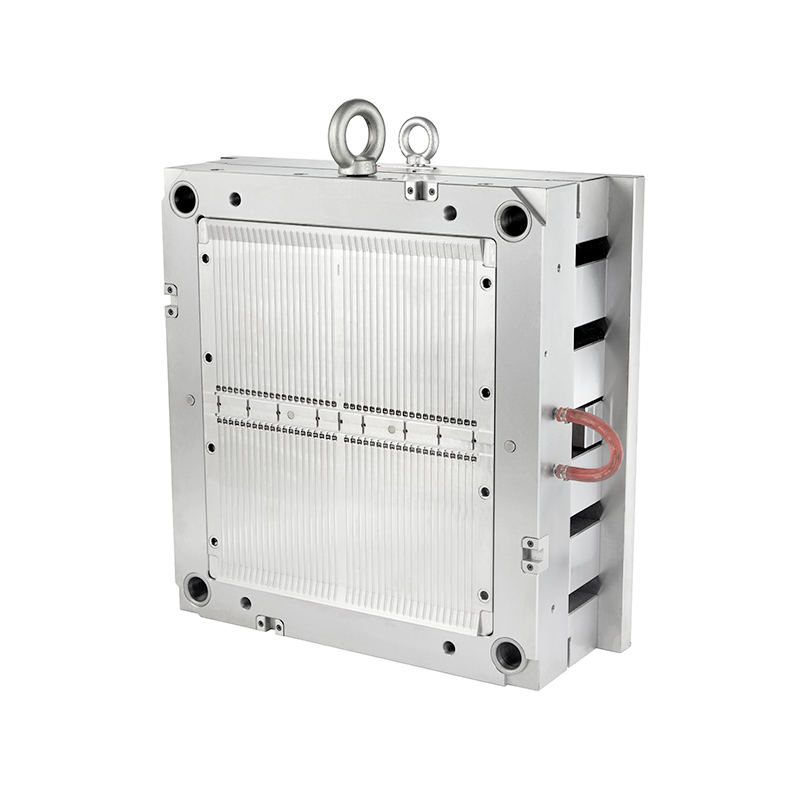

There are several types of cable tie moulds available, each designed to cater to different production needs. The common types are as follows:
1. Single-Cavity Moulds
A single-cavity mould is designed to produce one cable tie at a time. This type of mould is often used for low-volume production or for highly specialized cable tie designs. While the production speed may be slower compared to multi-cavity moulds, single-cavity moulds are ideal for smaller batches or when producing cable ties with unique dimensions or features.
Advantages:
Flexibility: Single-cavity moulds are often more customizable, allowing for the creation of specialized or unique cable ties.
Lower Initial Investment: Due to the simpler design, single-cavity moulds tend to have a lower initial cost compared to more complex multi-cavity moulds.
Disadvantages:
Lower Production Speed: Because only one cable tie is produced at a time, the cycle time is slower compared to multi-cavity moulds.
Higher Per-Unit Cost: For large-scale production, the per-unit cost of manufacturing cable ties with a single-cavity mould can be higher than with multi-cavity moulds.
2. Multi-Cavity Moulds
Multi-cavity moulds are designed to produce multiple cable ties in a single cycle. These moulds can have anywhere from two to dozens of cavities, depending on the production requirements and the size of the cable tie. Multi-cavity moulds are commonly used in high-volume manufacturing, where speed and efficiency are essential.
Advantages:
Increased Production Efficiency: By producing several cable ties per cycle, multi-cavity moulds significantly reduce production time and increase output.
Lower Per-Unit Cost: The per-unit cost is generally lower for high-volume production, making multi-cavity moulds ideal for large orders.
Disadvantages:
Higher Initial Cost: Multi-cavity moulds are more expensive to design and manufacture due to their complexity.
Limited Customization: While multi-cavity moulds can produce standard cable ties efficiently, they may not offer the same flexibility as single-cavity moulds for highly specialized designs.
3. Hot Runner Moulds
Hot runner moulds use a heated system to keep the plastic material in a molten state throughout the injection process. This allows for more precise control of the material flow and reduces waste. Hot runner moulds are commonly used for producing high-quality, high-volume cable ties, especially when consistency is a key concern.
Advantages:
Reduced Waste: Since the plastic material remains molten in the hot runner system, there is minimal material waste, bring about cost savings and environmental benefits.
Improved Cycle Time: Hot runner systems help speed up the injection moulding process, bring about faster cycle times and higher production rates.
Higher Precision: Hot runner moulds offer better control over the injection process, bring about more accurate and consistent cable ties.
Disadvantages:
Higher Initial Cost: The design and manufacturing costs of hot runner moulds are higher compared to cold runner systems, making them more suitable for large-scale production.
Maintenance Costs: Hot runner systems require more frequent maintenance due to the complexity of the heated system.
4. Cold Runner Moulds
Cold runner moulds rely on a cooling system to solidify the plastic material after it has been injected into the mould cavities. Unlike hot runner systems, the plastic material in a cold runner system solidifies before being ejected from the mould, which means that additional material, known as the runner, is typically discarded or recycled.
Advantages:
Lower Initial Cost: Cold runner moulds are generally less expensive to design and manufacture than hot runner moulds.
Simplicity: Cold runner systems are simpler and easier to maintain than hot runner systems, making them a more cost-effective option for certain applications.
Disadvantages:
Material Waste: Cold runner moulds tend to produce more material waste, as the runner system is often discarded or recycled, which can increase production costs.
Slower Production Rates: Cold runner moulds may have longer cycle times than hot runner systems, resulting in lower production rates.