 2025.09.12
2025.09.12
 News
News
A PP seal cable tie mold is used to manufacture cable ties that include a sealing mechanism, often employed in securing cables and wires while also ensuring a tight, tamper-proof fit. These cable ties are often used in critical applications where safety, security, or a secure fit is required, such as in industrial electrical installations or data centers.
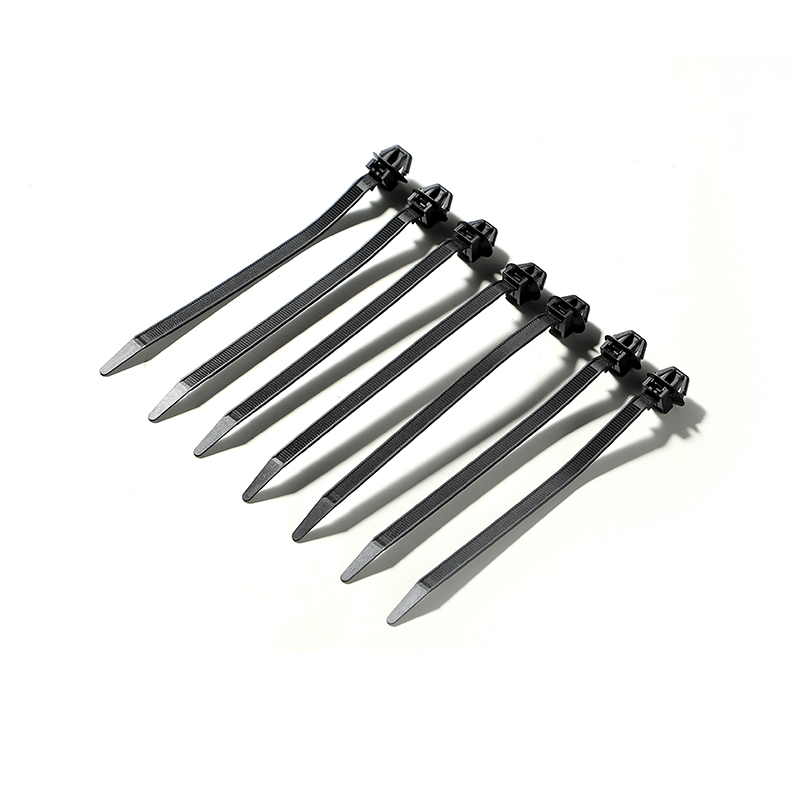

The PP material, polypropylene, is a thermoplastic polymer commonly used in cable tie production due to its strength, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. The molding process for producing PP seal cable ties involves creating intricate shapes with the help of molds designed to match the specifications for size, durability, and functionality.
Materials Used in PP Seal Cable Tie Molds
The choice of material for a PP seal cable tie mold is crucial in ensuring the durability, performance, and quality of the final product. Below are the materials commonly used in the production of PP seal cable tie molds.
1. Steel Alloys
Steel alloys, specifically high-quality tool steels, are the primary material used for making PP seal cable tie molds. These steels are selected for their ability to withstand the high pressure and temperature conditions encountered during the injection molding process.
Hardened Tool Steel: Tool steels such as P20, H13, or S136 are commonly used for molds that require durability and resistance to wear. Hardened tool steels provide excellent hardness, ensuring that the mold can endure repeated use without deteriorating.
Corrosion-Resistant Steel: In some cases, corrosion-resistant steels, such as stainless steel, are used for the molds. This is particularly important when the molds are exposed to aggressive cleaning agents or moisture, as it ensures the longevity of the mold and prevents rust and corrosion that could affect the precision of the mold.
2. Aluminum Alloys
Aluminum alloys are also sometimes used in PP seal cable tie molds, especially for prototypes or smaller-scale production runs. Aluminum molds are lighter and more cost-effective compared to steel molds, and they can be machined more easily.
Advantages of Aluminum: Aluminum molds offer faster turnaround times due to their quicker machining process. While they may not be as durable as steel molds for large-scale production, they provide a viable option for low-volume or experimental production where cost and speed are crucial factors.
Cost-Effective and Lightweight: Aluminum molds are often used in industries where prototype testing or smaller production runs are required. The relatively lower cost and reduced weight of aluminum molds make them ideal for these types of applications.
3. Plastic Inserts
For specific areas of the mold, plastic inserts may be used to create precise cavities or to reduce wear and tear on parts that are subject to frequent use. These inserts may be made of high-strength polymers that can withstand the heat and pressure of the molding process while also offering greater flexibility.
Use of Plastic Inserts: These are often incorporated into parts of the mold that require intricate shapes or features. Plastic inserts can also help increase the efficiency of the molding process by reducing friction and improving the longevity of the mold.
The Production Process of PP Seal Cable Tie Molds
The production of PP seal cable tie molds follows a systematic process that involves several steps. Below are the key stages involved in creating these molds:
1. Design and CAD Modeling
The step in producing a PP seal cable tie mold is the design phase. Using computer-aided design (CAD) software, engineers create a detailed model of the cable tie mold, incorporating the desired dimensions, features, and specifications for the product. This model serves as the blueprint for the entire mold-making process.
Precise Design Considerations: The design must account for factors such as the thickness of the cable tie, the placement of the sealing mechanism, and the features needed for the PP material to flow properly during the injection molding process.
Simulation and Testing: Advanced simulation tools may be used to simulate the flow of the PP material during molding, ensuring that the mold design is optimized for smooth material flow and efficient cooling.
2. Mold Fabrication and Tooling
Once the design is finalized, the fabrication of the mold begins. This step involves cutting, shaping, and assembling the various components of the mold. Tooling is performed with high-precision machines such as CNC (computer numerical control) machines, EDM (electrical discharge machining), and other advanced manufacturing equipment.
Milling and Drilling: CNC machines are used to mill and drill the mold components to precise dimensions, ensuring that the mold cavities match the design specifications accurately.
EDM for Fine Details: Electrical discharge machining is often used for creating intricate details and precise features in the mold, such as the locking mechanisms for the seal cable tie.